Human anatomy muscles - Head and neck muscles
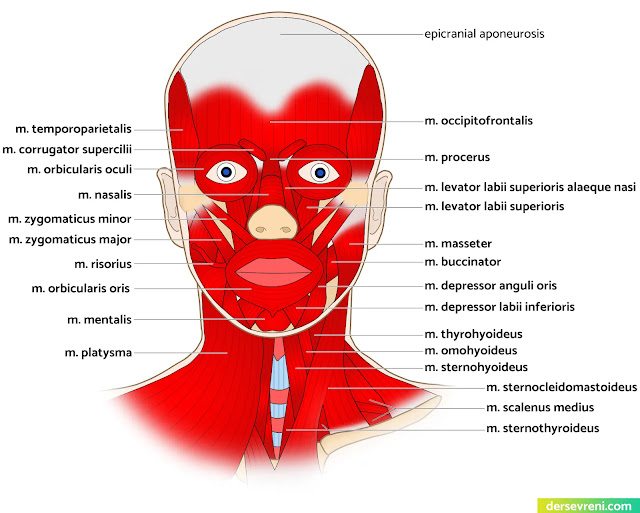
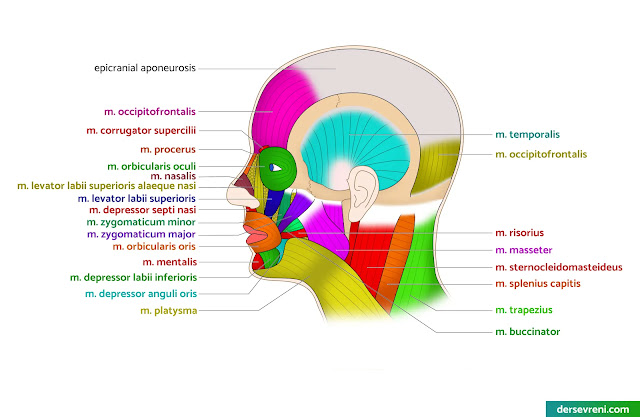
1- Facial muscles mm. fasciei
A- Facial muscles around the mouth:
- orbicularis oris muscle
- It is a group of muscles that surround and move the lips. It helps to change the shape of the lips and to close and open the lips.
- levator labii superioris muscle
- It allows the upper lip to rise.
- levator anguli oris muscle
- It causes the corner of the mouth to rise.
- zygomaticus major muscle
- It is a muscle located in the cheeks that helps with smiling. It is a large muscle group located under the cheekbone.
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- It is a small muscle located in the cheeks that helps with smiling. It is a small group of muscles located under the cheekbone.
- risorius muscle
- It enables the grin. It is a muscle that helps pull the lips sideways. It is a small muscle group located at the corners of the mouth.
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- It enables frowning. It is a muscle that helps pull the corner of the lip downwards. It is a small muscle group located under the lower jaw bone.
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- It enables pouting. It is a muscle that helps pull the lower lip downwards. It is a small muscle group located under the lower jaw bone.
- buccinator muscle
B- Facial muscles around the eyes:
- orbicularis oculi muscle
- It is a muscle that helps open and close the eyelids and blink. It is a circular muscle group located around the eye. It is innervated by several nerves that control the movement of the eyelids.
- corrugator supercilii muscle
- It is a muscle that pulls the eyebrows downwards, causing a frown. It is a small, thin muscle group located under the nasal bone. It is stimulated by the nerves that control facial expression.
- depressor supercilii muscle
- It is a muscle that helps pull the eyebrows down. It is a small group of muscles located above the orbital bone. It is innervated by the nerves that control facial expression.
- levator palpebrae superioris muscle
- A muscle that helps open the eye by lifting the upper eyelid. A small group of muscles located behind the eye. It is stimulated by the nerves that control eye movement.
C- Facial muscles around the nose:
- nasalis muscle
- It is a muscle located on and next to the nose.
- It consists of two parts:
- alar section (alar section of the nasal muscle): Expands the wings of the nose.
- Transverse part (transverse part of the nasal muscle): Narrows the nostril.
- procerus muscle
- It is a muscle located under the nasal bone.
- It pulls the skin downward along the bridge of the nose. This plays a role in the frowning movement.
- depressor septi muscle
- It is a muscle that attaches to the nasal septum.
- It pulls the nasal septum downward.
D- Scalp muscles:
- occipitofrontalis muscle
- It is a muscle that covers the upper part of the head.
- It consists of two parts:
- venter occipitalis (occipital part of the occipitofrontalis muscle): Attaches to the occipital bone and moves the forehead skin upward and backward.
- venter frontalis (frontal division of the occipitofrontalis muscle): Attaches to the frontal bone and moves the skin of the forehead upward and forward.
- temporoparietal muscle
- It is a muscle located on the side of the head.
- It consists of two parts:
- venter temporoparietalis (temporal division of the temporoparietalis muscle): Attaches to the temporal bone and moves the forehead skin upward and laterally.
- venter parietalis (parietal division of the temporoparietal muscle): Attaches to the parietal bone and moves the skin of the forehead upward and backward.
E- Facial expression muscle in the neck:
• m. platelet
-------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------- -
2-Masturative muscles - mm. masticatorii
- masseter muscle (external masticatory muscle): lifts the mandible and closes the mouth.
- temporalis muscle (temporal muscle): It is the strongest chewing muscle, closes the mouth and lifts the mandible.
- medial pterygoideus muscle (medial lateral wing muscle): elevates the mandible and pulls it to the opposite side during chewing.
- pterygoideus lateralis muscle (lateral wing muscle): Opens the jaw and pulls the mandible to the right and left.
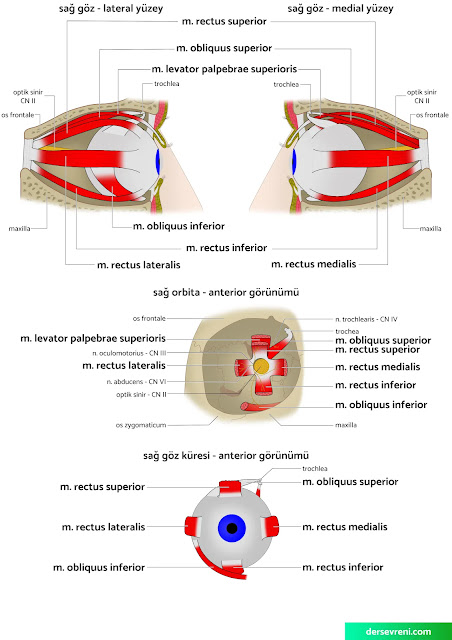
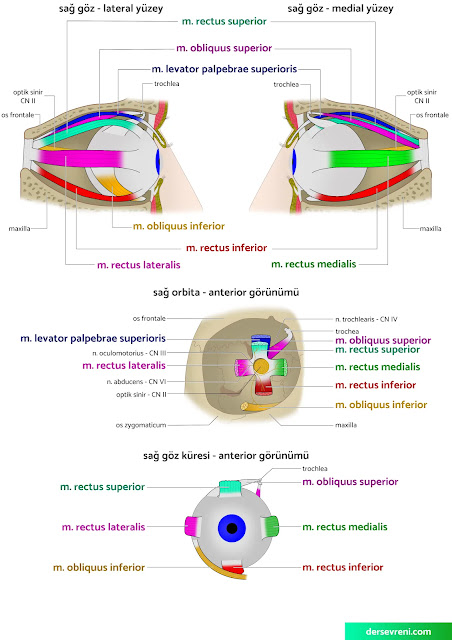
3- Eye muscles
- rectus superior muscle: Moves the eyeball upwards. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as looking up, keeping the eyes fixed while reading or writing, and looking at objects upwards,
- rectus inferior muscle: Moves the eyeball downwards. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as looking downwards, preventing the eyes from shifting upwards when writing, and looking at downward objects,
- rectus lateralis muscle: Moves the eyeball outward. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as looking to the side, allowing the eyes to see both sides of the road while driving, and looking at wide areas,
- rectus medialis muscle: Moves the eyeball inward. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as bringing the eyes closer to the nose, allowing the oncoming vehicles to be noticed, and looking at close objects.
- obliquus superior muscle: Moves the eyeball outward and upward. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as looking up and to the left, perceiving three-dimensional objects, and looking at heights,
- obliquus inferior muscle: Moves the eyeball inward and downward. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as looking down and to the left, perceiving three-dimensional objects, and looking down.
4- Tongue muscles
intrinsic muscles of the tongue
- longitudinalis superior linguae muscle (superior longitudinal tongue muscle): Runs along the length of the tongue and moves the tongue upwards and backwards. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as speech, swallowing and chewing.
- longitudinalis inferior linguae muscle (inferior longitudinal tongue muscle): Runs along the length of the tongue and moves the tongue downward and forward. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as speech, swallowing and chewing.
- transversus linguae muscle (transverse muscle of the tongue): extends diagonally under the tongue and shortens the tongue. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as speech, swallowing and chewing.
- verticalis linguae muscle (vertical muscle of the tongue): Extends vertically from the center of the tongue and elevates the tongue. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as speech, swallowing and chewing.
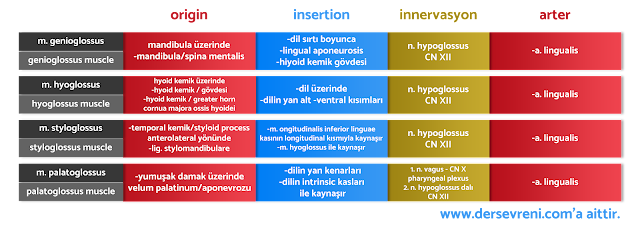
extrinsic muscles of the tongue
- genioglossus muscle: Pushes the tongue forward. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as speech, swallowing and chewing.
- hyoglossus muscle: Pulls the tongue downwards. This muscle helps move the tongue towards the floor of the mouth.
- styloglossus muscle: Pulls the tongue upward and backward. This muscle helps move the tongue toward the roof of the mouth.
- palatoglossus muscle: Allows the tongue to move towards the soft palate. This muscle plays an important role in actions such as swallowing and speaking.
-------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------- -
5- Nape muscles
Deep nape muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle (large posterior rectus muscle): A muscle located at the back of the head, allowing the head to move up and back. This muscle allows the head to stand upright and support the spine.
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle (small posterior rectus muscle): A muscle located at the back of the head that allows the head to move upwards and backwards. This muscle works together with m. rectus capitis posterior major muscle and contributes to the stability of the head.
- obliquus capitis superior muscle (superior oblique head muscle): It is a muscle located on the side of the head and allows the head to move sideways. This muscle allows the head to rotate on the shoulders.
- obliquus capitis superior muscle (inferior oblique head muscle): A muscle located on the underside of the head that allows the head to move sideways. This muscle works together with m. obliquus capitis superior muscle and contributes to the stability of the head.
Neck and nape muscles
Cervical muscles
- platysma muscle: A thin, flat muscle covering the lower part of the face. It pulls the corners of the mouth down, moves the chin down and forward, and tightens the skin of the neck.
- sternocleidomastoideus muscle: Two long, thin muscles that move the neck and head. They move the head forward, sideways and downward.
- longus capitis muscle: A muscle located at the front of the neck. It allows the head to move forward.
- longus colli muscle: It is a muscle located on the front and sides of the neck. It allows the head to move forward and sideways.
- scale muscles
- m. scalenus anterior: Allows the head to move forward and sideways.
- m. scalenus posterior: Allows the head to move forward and sideways.
- m. scalenus medius: Allows the head to move forward and sideways.
- rectus capitis anterior muscle: It is a muscle located at the front of the neck. It allows the head to move forward.
- rectus capitis lateralis muscle: A muscle located on the side of the neck. It allows the head to move sideways.
Suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis superior muscle
- rectus capitis posterior muscle
- m. rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- m. rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis muscle
- m. obliquus capitis superior muscle
- m. obliquus capitis inferior muscle
Suprahyoid muscles- Suprahyoid muscles
- digastric muscle
- stylohyoideus muscle
- mylohyoideus muscle
- genioglossus muscle
Subhyoid muscles- Infrahyoid muscles
- sternohyoid muscle:
- It is a long, thin muscle that extends from the sternum to the hyoid bone.
- Moves the hyoid bone downward.
- sternothyroideus muscle
- It is a long, thin muscle that extends from the sternum to the thyroid cartilage.
- It moves the thyroid cartilage downward.
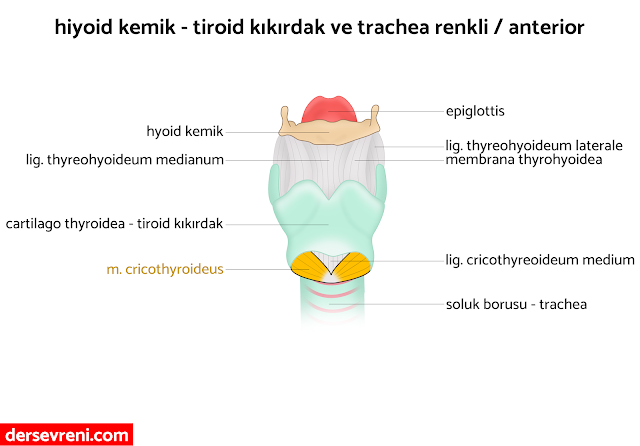
- thyrohyoideus muscle
- It is a long, thin muscle that extends from the thyroid cartilage to the hyoid bone.
- Moves the hyoid bone upwards.
- omohyoideus muscle
- It is a two-headed muscle that extends from the clavicle to the hyoid bone.
- It moves the hyoid bone downward.
Subhyoid muscles- Infrahyoid muscles - m. sternohyoideus m. sternothyroideus m. thyrohyoideus m. omohyoideus
- It is a long, thin muscle that extends from the sternum to the hyoid bone.
- Moves the hyoid bone downward.
- It is a long, thin muscle that extends from the sternum to the thyroid cartilage.
- It moves the thyroid cartilage downward.
- It is a long, thin muscle that extends from the thyroid cartilage to the hyoid bone.
- Moves the hyoid bone upwards.
- It is a two-headed muscle that extends from the clavicle to the hyoid bone.
- It moves the hyoid bone downward.
-------------------------------------------------- -------------------------------------------------- -
pharynx and larynx muscles
pharynx muscles
- constrictor pharyngitis muscle
- m. constrictor pharyngis superior
- m. constrictor pharyngis medius
- m. constrictor pharyngis inferior
- salpingopharyngeus muscle
- It is a muscle that connects the eustachian tube of the middle ear to the svelgel.
- It allows the eustachian tube to open during swallowing. This helps balance the pressure in the middle ear.
- palatopharyngeus muscle
- It is a muscle that attaches to the soft palate and the palatine.
- It allows the soft palate to rise and the svelgel to narrow during swallowing, facilitating the downward movement of swallowed food and liquids.
- stylopharyngeus muscle
- It is a muscle that extends from the styloid process to the svelgel.
- It allows the svelgel to contract and move upwards. This facilitates the downward movement of swallowed food and liquids.
- levator veli palatini muscle
- It is a muscle that attaches to the soft palate.
- It allows the soft palate to rise and the svelgel to narrow during swallowing, facilitating the downward movement of swallowed food and liquids.
- tensor veli palatini muscle
- It is a muscle that attaches to the soft palate.
- It causes the soft palate to tighten, making it easier for swallowed food and liquids to move downward.
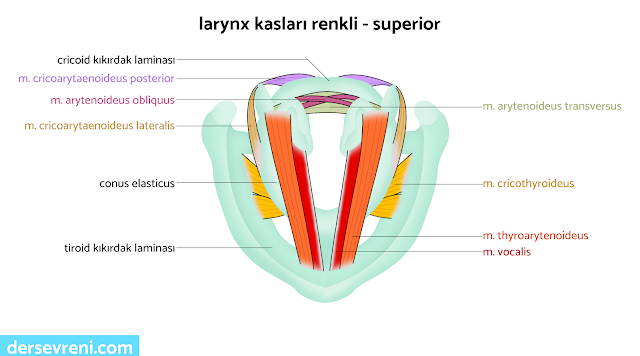
Larynx muscles
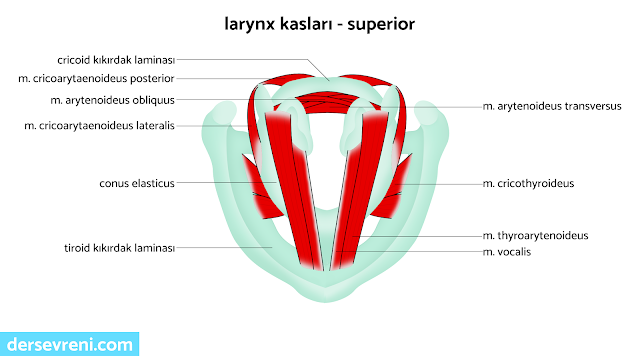
- cricothyroideus muscle
- It is a muscle that extends from the cricoid cartilage to the thyroid cartilage.
- It adjusts the tension of the vocal cords by changing the anterior-posterior diameter of the thyroid cartilage.
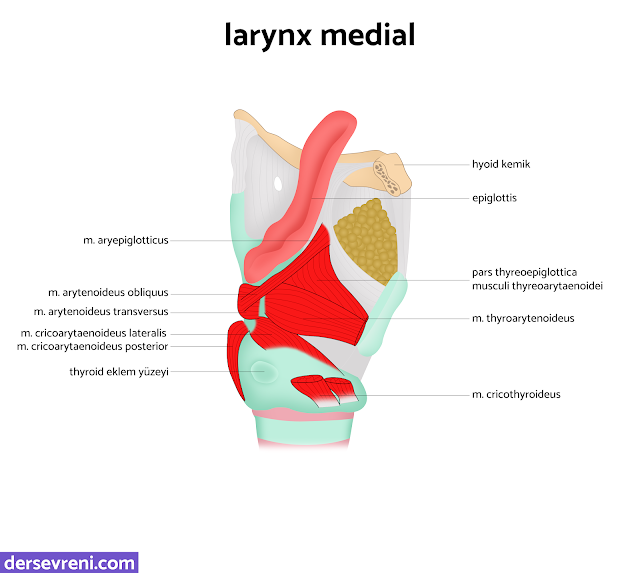
- cricoarytenoideus muscle
- cricoarytenoideus posterior muscle: It is a muscle that extends from the cricoid cartilage to the arytenoid cartilage. It moves the arytenoid cartilage backwards and allows the vocal cords to open.
- cricoarytenoideus lateralis muscle: It is a muscle that extends from the cricoid cartilage to the arytenoid cartilage. It moves the arytenoid cartilage forward and enables the vocal cords to close.
- m.arytenoideus muscle
- aryntenoideus obliquus muscle: It is a muscle that extends from one end of the arytenoid cartilage to the other. It allows the rotation of the arytenoid cartilage.
- aryntenoideus transversus muscle: It is a muscle that changes the anterior-posterior diameter of the arytenoid cartilage.It adjusts the tension of the vocal cords.
- thyroarytenoideus muscle
- vocal muscle: It is a muscle extending from the top of the arytenoid cartilage. It regulates the quality and intensity of the voice by tightening the vocal cords.
- Thyroarytenoideus muscle: A muscle extending from the thyroid cartilage to the epiglottis. It allows the epiglottis to move downward. This helps prevent food from entering the respiratory tract during swallowing.







.png)
.png)
.png)



.png)










Yorum Gönder